Christian Funeral Traditions Beyond Catholicism: Protestant, Anglican, and Orthodox Practices
Christian funeral traditions share a foundation in the belief in eternal life, the resurrection of the dead, and honoring the deceased with dignity. While Catholic funerals follow a structured liturgy rooted in Roman Catholic doctrine, other major Christian branches—including Eastern Orthodoxy, Anglicanism, and mainline Protestantism—observe their own meaningful and theologically rich customs.
According to the Pew Research Center (2021), approximately 40% of U.S. adults identify as Protestant, encompassing a wide range of denominations such as Methodists, Baptists, Lutherans, Pentecostals, Episcopalians, and others. Additionally, about 1% identify with Orthodox Christianity, including Greek, Russian, and other Eastern Orthodox traditions. Together, these groups represent a significant portion of the religious landscape in the United States and influence diverse Christian funeral customs across the country.
In this article, we explore the funeral practices of these Christian denominations, highlighting both their spiritual significance and ritual expressions.
Eastern Orthodox Funerals
A. Theological Foundations
In Eastern Orthodoxy, death is viewed as a passage into eternal life. Funerals emphasize the soul’s journey and the importance of prayers for the departed. Orthodox theology teaches that although the body dies, the soul remains conscious and awaits the final resurrection.
B. Ritual Elements
According to the Greek Orthodox Archdiocese of America, the funeral service typically includes:
- Psalms, hymns, and scriptural readings
- The Trisagion service (a short service of prayers for the deceased)
- A viewing or wake, often accompanied by chanting
- The final Kiss of Peace, where mourners say goodbye
Burial is strongly preferred, and cremation is generally discouraged within Orthodoxy.
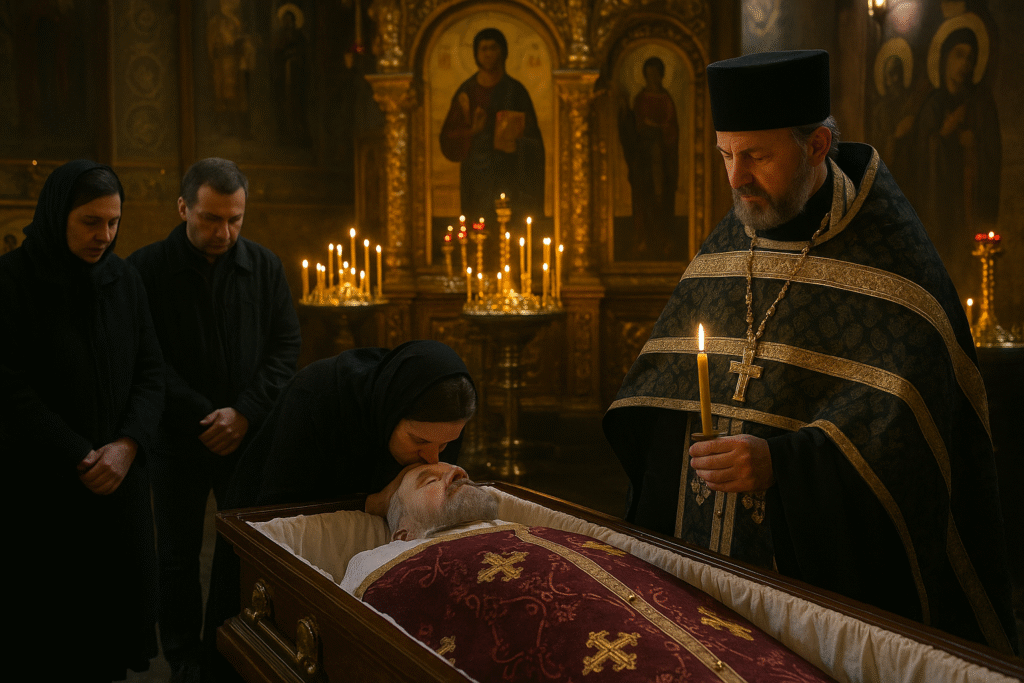

A priest leads the final prayers as mourners offer the Kiss of Peace during a traditional Eastern Orthodox funeral inside a candlelit church adorned with gilded icons.
Anglican (Episcopal) Funerals
The Episcopal Church follows the Book of Common Prayer, which provides a full liturgy for The Burial of the Dead, structured around hope in the resurrection.
The liturgy includes:
- A procession into the church
- Biblical readings, psalms, and a homily
- The celebration of Holy Eucharist (optional)
- Commendation and committal at the grave or cremation site
The service is designed to affirm faith while also allowing space for mourning and remembrance.
Methodist Funerals (United Methodist Church)
In Methodist tradition, funerals are often called Services of Death and Resurrection. The name reflects the dual purpose of honoring the life of the deceased while proclaiming the hope of resurrection.
According to the United Methodist Church Discipleship Ministries, services usually include:
- Prayers of thanksgiving for the life of the deceased
- Scripture readings (especially from Romans and John)
- A short sermon or reflection
- Hymns and musical tributes
- An optional Eucharist
Both cremation and burial are accepted within Methodist communities.
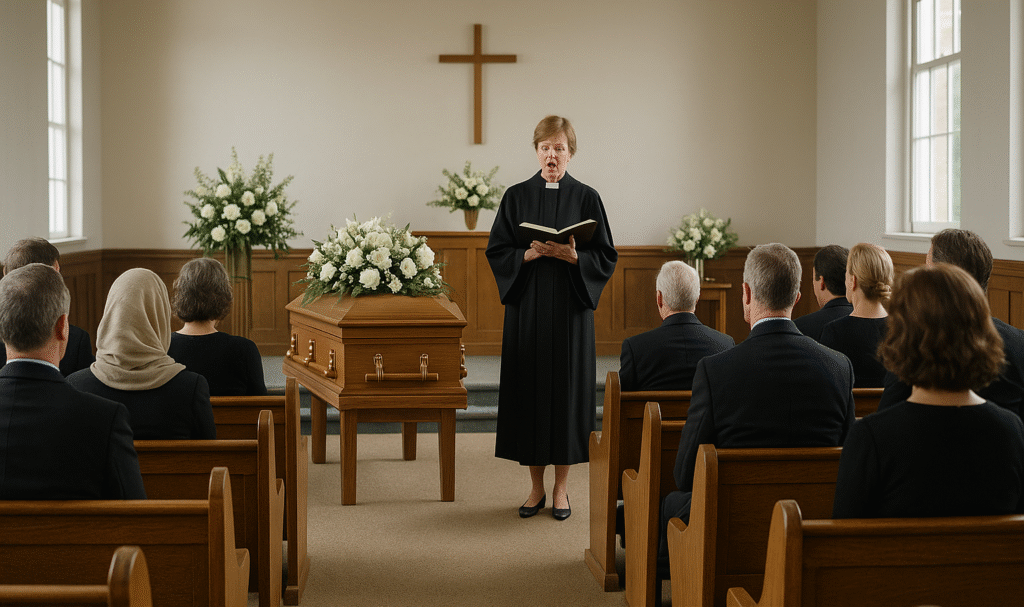
A female minister delivers a eulogy during a Methodist funeral, as mourners gather in a simple church adorned with white flowers and a wooden cross.
Methodist Church (UK)
The Methodist Church in the UK encourages a flexible structure, balancing tradition with personal elements.
Core elements include:
- A welcome and prayer
- Readings and eulogy
- A period of silence or personal reflection
- Hymns or music
- A commendation and farewell
The Methodist Church recognizes cremation as a valid and respectful option. Services may take place in a church, chapel, crematorium, or graveside.
Orthodox Church in America (OCA)
The OCA teaches that the funeral serves three purposes:
- To pray for the repose of the departed soul
- To comfort the living
- To affirm belief in the resurrection
OCA funerals closely follow traditional liturgy, with the Panikhida (memorial service), chanted Psalms, and Gospel readings. Mourners often participate actively through responses and prayers.
Final Thoughts
While the styles and emphases differ across Christian denominations, each tradition upholds the dignity of the deceased, offers spiritual comfort to the bereaved, and expresses the central Christian hope of resurrection. Whether in the solemn chants of the Orthodox Church, the liturgical beauty of Anglicanism, or the simplicity and grace of Methodist rites, funeral customs reflect each denomination’s theology and cultural heritage.
At Anubis Cremations, we are committed to honoring the diversity of Christian traditions with respect, flexibility, and care.
Contact us
-Los Angeles: (323) 644-3323
-Palm Springs: (760) 804-3323
-Email: info@anubiscremations.com
References
- Greek Orthodox Archdiocese of America. (n.d.). The funeral service of the Orthodox Church.
Retrieved from: https://www.goarch.org/-/the-funeral-service-of-the-orthodox-church - The Episcopal Church. (n.d.). Burial of the Dead: Rite I (Book of Common Prayer).
Retrieved from: https://www.bcponline.org/PastoralOffices/BurialI.html - United Methodist Church – Discipleship Ministries. (2014). A Service of Death and Resurrection.
Retrieved from: https://www.umcdiscipleship.org/resources/a-service-of-death-and-resurrection - The Methodist Church (UK). (n.d.). Funerals.
Retrieved from: https://www.methodist.org.uk/faith/life-and-faith/life-events/funerals/ - Orthodox Church in America. (n.d.). The Orthodox Faith: Death, Burial, and the Orthodox Funeral.
Retrieved from: https://www.oca.org/orthodoxy/the-orthodox-faith/worship/the-sacraments/funeral





